Pretty Diagrams
A visual overview of CommandBox server deployments for both singular and Multi-Site configurations
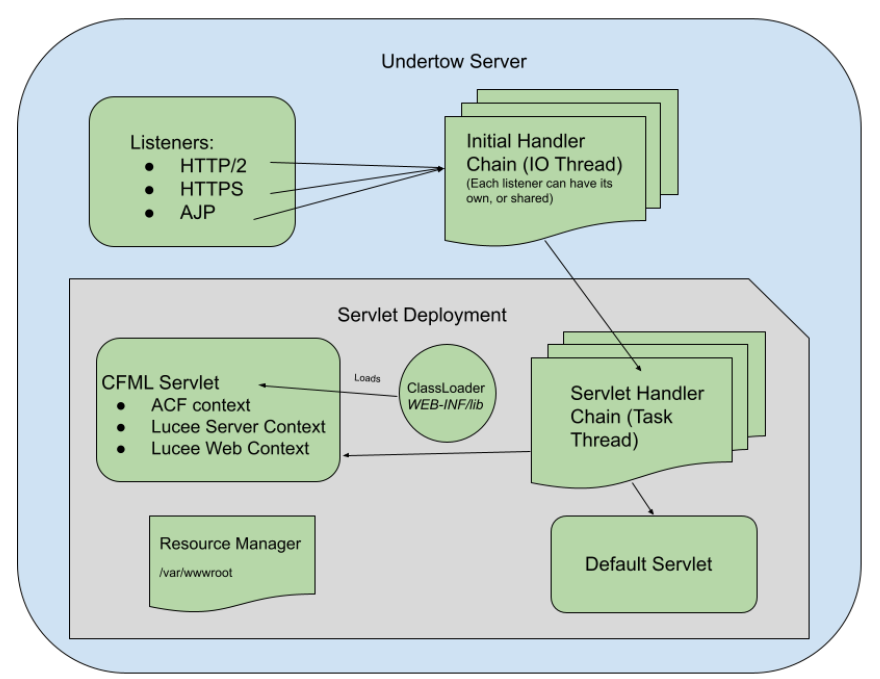
CommandBox's Servlet configuration
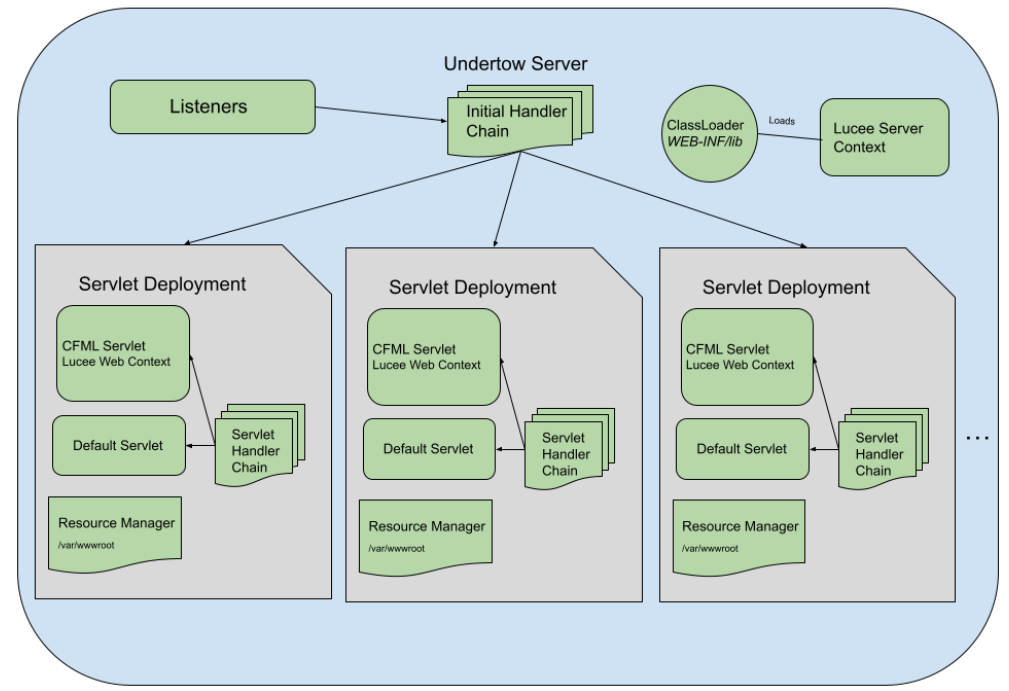
CommandBox Multi-Site with Lucee
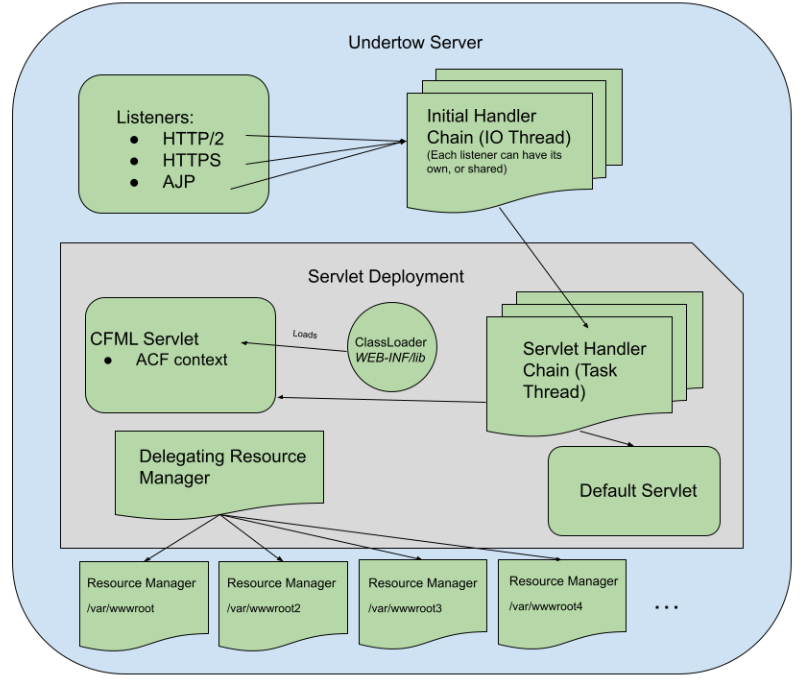
CommandBox Multi-Site with Adobe CF
Was this helpful?